ART MADRID CLOSES ITS 21ST EDITION AS A KEY EVENT OF MADRID ART WEEK
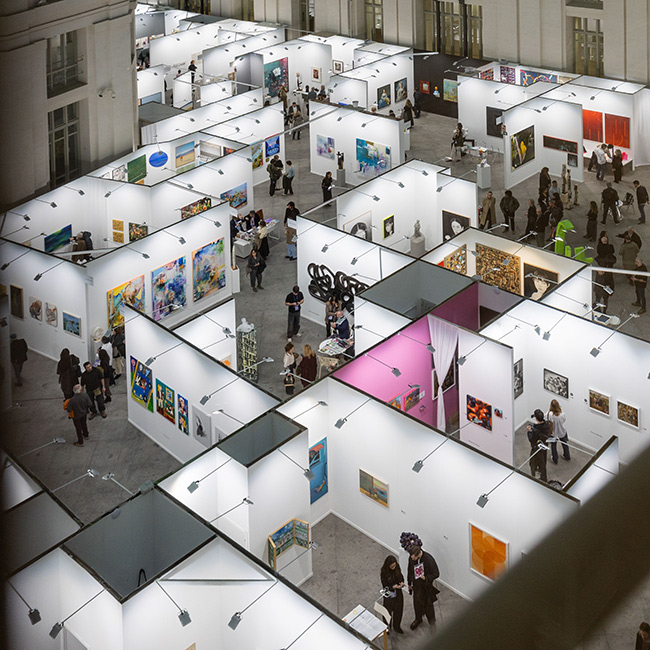
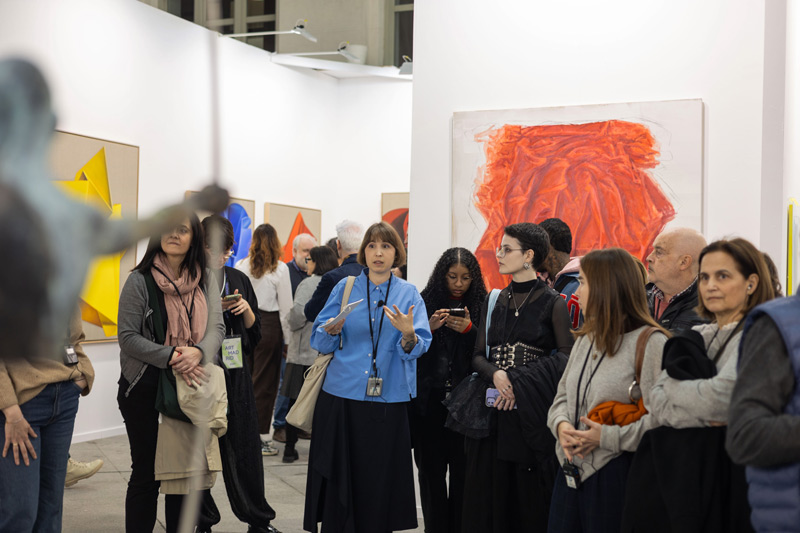
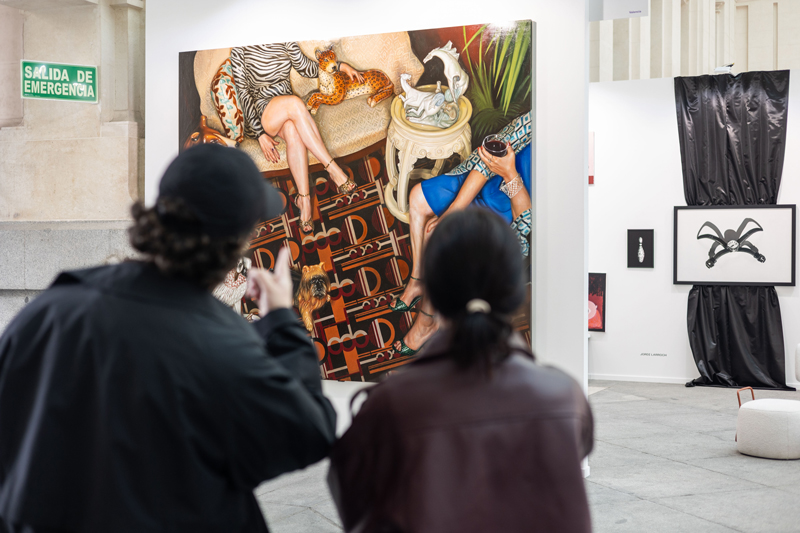
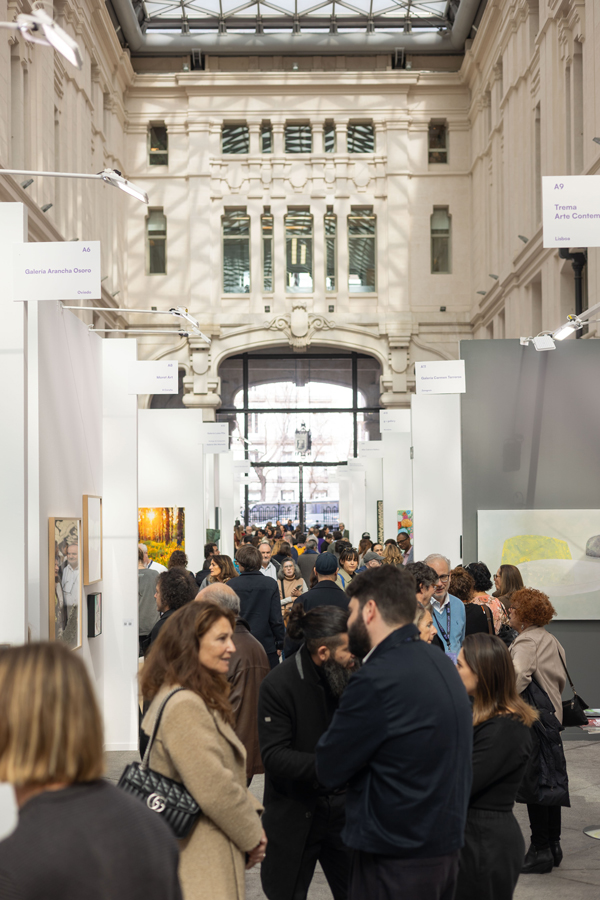
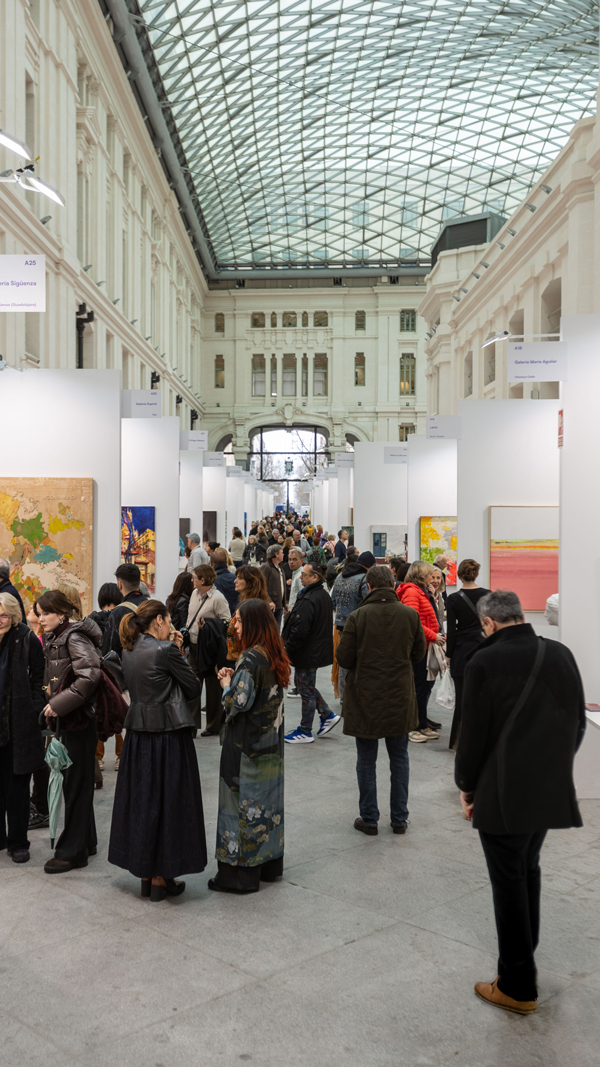
The Galería de Cristal of the Palacio de Cibeles hosted the 21st edition of Art Madrid from March 4 to 8, once again consolidating its role as one of the must-see events of Madrid Art Week. Over the course of five days, the fair brought together 35 national and international galleries and more than 200 artists, turning the venue into a meeting point for gallerists, collectors, professionals, and lovers of contemporary art.
Throughout its trajectory, Art Madrid has built a distinct identity, with a constant focus on giving visibility to both emerging and established galleries and on opening contemporary art to diverse audiences. Rather than being structured around a single curatorial line, the fair embraced a plural proposal, respecting the unique DNA of each exhibitor.
Art Madrid’26 presented a Gallery Program distinguished by the diversity of artistic proposals and languages, encouraging dialogue between different generations and contemporary practices. Painting, sculpture, photography, drawing, installation, and new hybrid forms coexisted in an edition that once again confirmed the dynamism of today’s art scene
During the days of the fair, nearly 20,000 visitors explored the booths of the participating galleries and enjoyed a parallel program that expanded the experience beyond the traditional exhibition format.
The Parallel Program: An Expanded Art Fair
The Parallel Program once again took center stage in the Art Madrid experience, activating the fair space through projects that explored new forms of interaction between artworks, artists, and the public.
Among the most notable initiatives was the performance series Open Infinite: What the Body Remembers, which presented a daily performative action at the fair featuring works by Colectivo La Burra Negra, Rocío Valdivieso, Amanda Gatti, and Jimena Tercero. The pieces incorporated the body as a critical device and a space of memory, reinforcing the presence of performance within Art Madrid’s programming.
The third edition of Open Booth presented Despiece. Protocolo de mutación, by Daniel Barrio, a site-specific project that transformed the booth into a landscape constructed from urban remnants and industrial materials. The installation invited visitors to physically engage with the work, creating an immersive experience within the exhibition space.
Meanwhile, Espacio Nebrija hosted the project Estancias transitorias (NotanIA SipedagogIE), a proposal by Nebrija University that reflected on Aesthetic Intelligence in the face of the growing dominance of algorithmic logic. The installation proposed a reclamation of gesture, materiality, and the time inherent to the creative process as dimensions that cannot be reduced to automation.
Lecturas. Curated Walkthroughs also returned, with itineraries designed by Zuriñe Lafón and Marisol Salanova that offered curatorial insights for exploring the fair from specific critical perspectives and expanding the visitor experience.
Patronage, Awards, and Acquisitions
Support for contemporary creation once again stood as one of the fair’s central pillars through the second edition of the Art Madrid Patronage Program, which recognizes the work of artists and strengthens the connections between galleries, collectors, and private entities.
On this occasion, the following awards were presented:
Cervezas Alhambra Emerging Artist Award
Iyán Castaño, represented by Galería Arancha Osoro
One Shot Hotels Breakthrough Artist Award
Joost Vandebrug, represented by KANT Gallery
In the Acquisition Awards category, several private collections incorporated works presented at the fair into their collections.
Studiolo Collection
Roger Sanguino — DDR Art Gallery
Devesa Law
Kim Han Ki — Banditrazos Gallery
E2IN2 Collection
Albert Bonet — Inéditad Gallery
dn2 Collection
Iván Baizán — Galería Arancha Osoro
These acquisitions reflect the private sector’s commitment to the development of contemporary art and contribute to advancing the professional trajectories of emerging and mid-career artists.
Collecting and Support for the Artistic Ecosystem
The promotion of collecting once again played a prominent role in this edition thanks to the One Shot Collectors program, which offered personalized advice to both new buyers and more experienced collectors, facilitating access to the contemporary art market and fostering direct relationships between artists, galleries, buyers, and collectors.
This program, together with the Patronage Program, continues to strengthen the professional ecosystem surrounding the fair and reinforce Art Madrid’s commitment to supporting contemporary creation.
Among the most notable sales were works by Antonio Ovejero, represented by CLC ARTE; Leticia Feduchi and Ángela Mena, represented by Galería Sigüenza; Idoia Cuesta and Iyán Castaño, represented by Galería Arancha Osoro; and Yasiel Elizagaray, represented by Nuno Sacramento Arte Contemporânea. Likewise, the proposals presented by Inéditad Gallery were very well received, with notable sales of works by artists Albert Bonet and Eduardo UrdIales, as well as Carmen Mansilla, who debuted at Art Madrid'26 and achieved a sold out.
The overall balance of the edition has been particularly positive, with sales reported by all 35 participating galleries, confirming the strong interest from collectors and the dynamism of the market throughout the fair. Among the galleries that recorded notable commercial activity are La Mercería (Valencia), LAVIO (Murcia–Shanghai), 3 Punts Galería (Barcelona), Galerie One (Paris), Shiras Galería (Valencia), Galería Rodrigo Juarranz (Aranda de Duero), Galería São Mamede (Lisbon), Yiri Arts (Taiwan), and Trema Arte Contemporânea (Lisbon), among others.
A Fair made possible thanks to Its network of Partners
The success of Art Madrid’26 has been made possible thanks to the support of its official sponsors: Cervezas Alhambra, One Shot Hotels, Liquitex, Universidad Nebrija, and Posca, as well as the trust of its collaborators: Asociación 9915, Colección Studiolo, E2IN2, Colección dn2, Devesa Law, Enviarte, Cova 13, and Vanille Bakery Lab & Café. The fair also benefits from the involvement of its media partners and the support of various cultural organizations, private collections, and institutions that contribute to strengthening the contemporary art ecosystem.
Art Madrid: A Future Full of Possibilities
After 21 years of history, Art Madrid continues to consolidate its position as a key event in the contemporary art calendar, both nationally and internationally. Its ability to bring together galleries, artists, collectors, and institutions reinforces its role as a space for encounter, exchange, and discovery. The fair maintains a steadily growing outlook, driven by a program that evolves each year and increasingly opens up to more innovative proposals.
Thank you for being part of the 21st edition of Art Madrid. Your support is essential for continuing to promote art and culture.
See You at Art Madrid’27!