La Quedada. Art Madrid'24 Studio Visits
Feb 9, 2024
art madrid
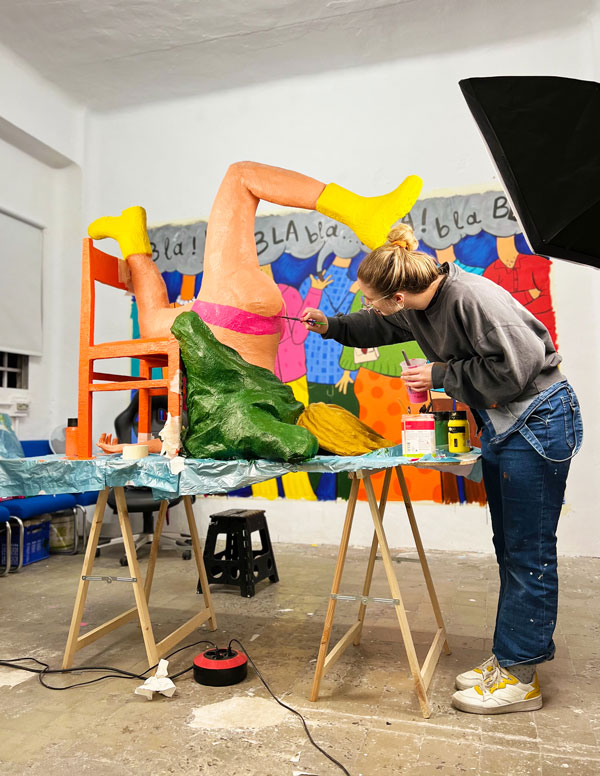
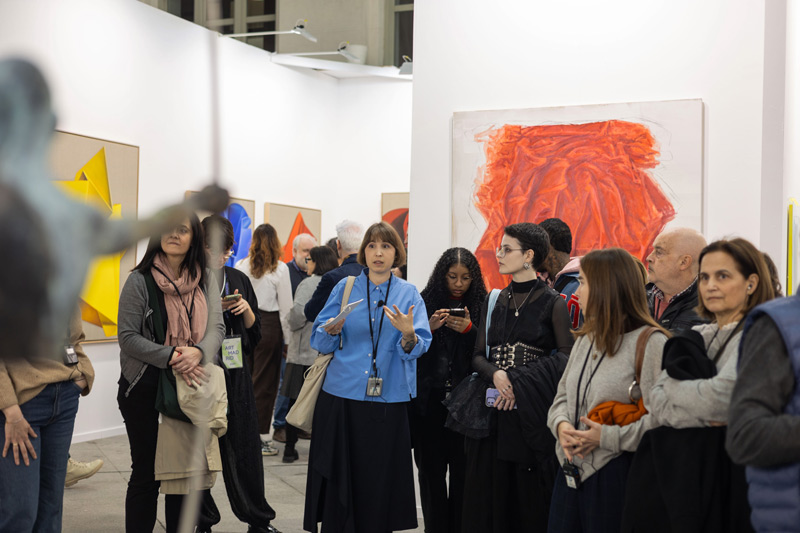
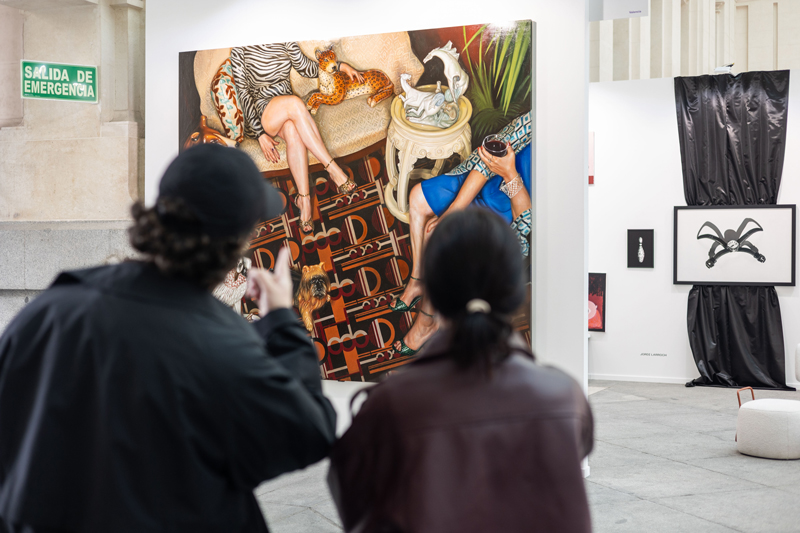
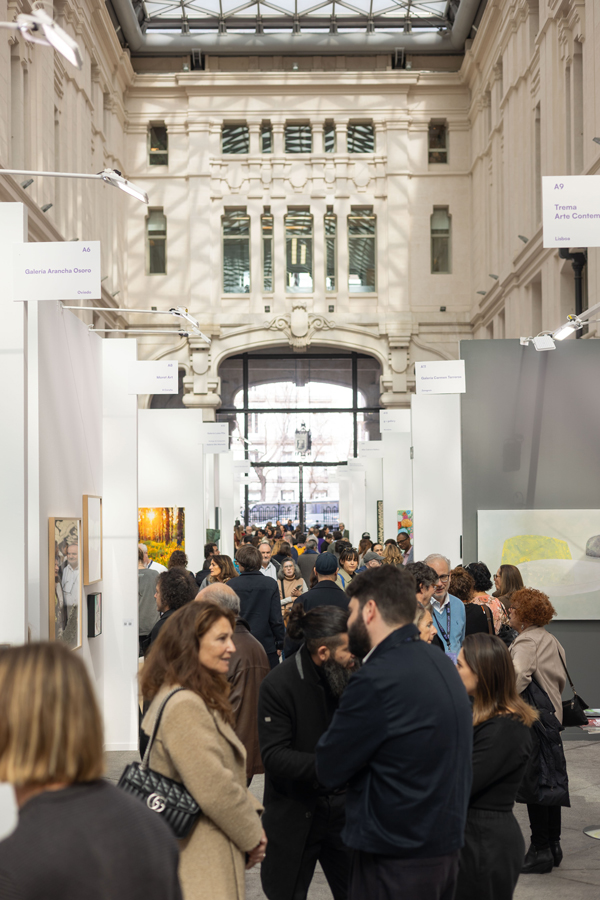
Getting together, making a plan to get to know each other and discovering an artist's workspace together can be an appealing proposal to start approaching the world of art. It is always a stimulus for the senses to enter a fertile ground for the imagination and to breathe the creative environment that usually surrounds these intimate spaces. To prove this, we have organized #LaQuedada, an itinerary through the studios of some of the artists who will participate in Art Madrid'24.
Have you ever wondered what an artist's workspace looks like? Have you ever imagined where an artist produces his or her work, for example when preparing to participate in an art fair?
It's very possible that you have unanswered questions. So, to help you discover this wonderful world of possibilities, we have organized #LaQuedada, an Art Madrid initiative to bring you closer to the surprising and sometimes romanticized world in which visual artists create.
A visit to an artist's studio is the perfect opportunity to get to know their aesthetic visions first hand and to be part of the experience of listening to them talk.We take the time to understand what their working methodologies are, what future projects they are working on, what the processes of their works are like, what materials they use to achieve those effects that we never imagined could be possible to produce... And so, among so much curiosity, we take a journey that reveals order and chaos, sketches and pigments, mutant ideas and possible utopias, notes and strokes that give shape to the vitality that each new project represents.
Artists are inspired by the experiences of their lives and their most intimate surroundings, and in their works they express the conflicts that torment them and the concerns they perceive in the society of which they are a part. Each of them represents an intimate, authentic, personal and yet shared truth. A common connection that unites us with them through the sensitivity with which we can identify if we look at them with other eyes: the eyes of the soul.
Today, being an artist in the art world is an act of courage. More and more artists are threatened by the precarious situation in our country today. That is why it is so important to support, promote and accompany artists. It doesn't matter if they are emerging artists or have been working in the art sector for part of their lives, what you should keep in mind is that you can contribute to the development of their career by acquiring some of their work; visiting their profiles on social networks and sharing their projects; attending galleries, fairs, cultural institutions or museums where they are exhibiting; or simply, connecting with the vitality of their artistic expressions in a visit to their studios.
We want #LaQuedada will be a recurring space that encourages open dialogue between the public and creators. A responsible way to promote the growth of the city's cultural structure is to make art accessible to all types of audiences. At Art Madrid we know this, and that is why today, more than ever, we want to bring contemporary art closer to everyone, trying to break the illusion that defines it as elitist and distances it from its humanist vocation. Creativity is everywhere and life is in the artist's studio.
In the first edition of #LaQuedada, we will have the opportunity to visit the studios of five artists participating in Art Madrid'24:
Carlos Tárdez - Galería Bea Villamarín
Elena Gual - Arma Gallery
Lara Padilla - Punts Galería
Richard García - Galería BAT Alberto Cornejo
Marina Tellme - Open Booth Art Madrid’24
La Quedada is a project designed for all audiences. Is possible thanks to ONE SHOT HOTELS, one of Art Madrid'24's official sponsors.
You can be part of it if you are a professional in the field of culture or if you are a passionate art lover. The duration of the visits will be approximately one and a half hours. If you are interested, you can find the calendar of activities on our website. You can also register by clicking on the button below.
ABOUT THE ARTISTS:
CARLOS TÁRDEZ (Madrid, 1976)
Multidisciplinary artist, in whose work has special importance the prominence of the message that is hidden in all his creations.In both painting and sculpture, he has achieved a level of quality that has earned him, among many other awards, the Medal of Honor of the BMW Painting Prize in 2010, 2018 and 2021.
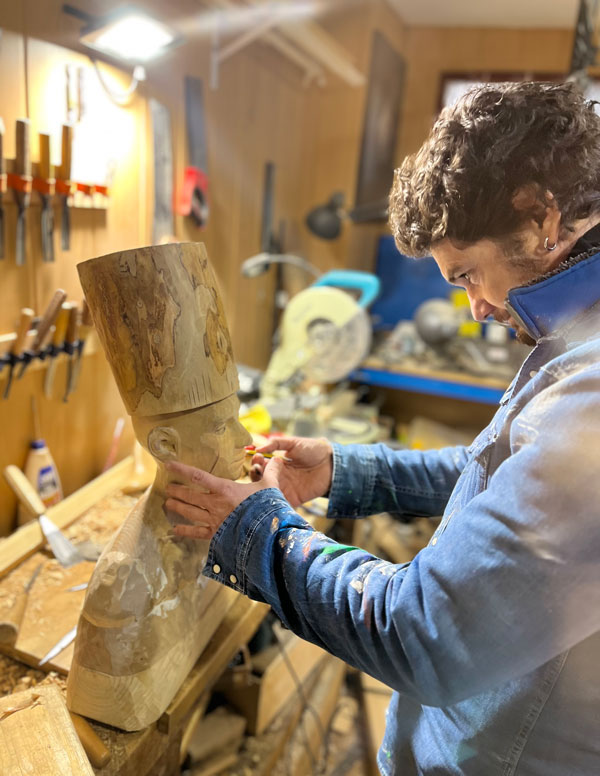

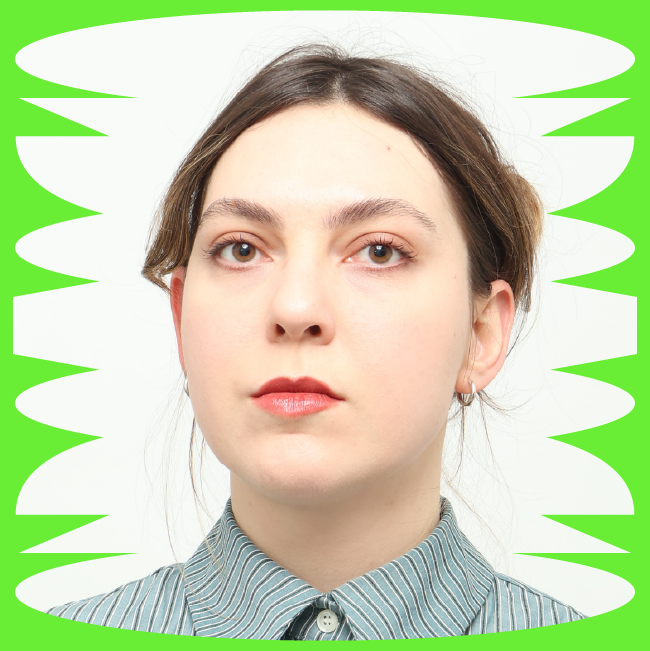
ELENA GUAL (Mallorca, 1994)
Elena Gual is known for her figurative paintings of women that celebrate their beauty and promote gender equality. Gual creates highly textured representations of skin, hair, and clothing by applying thick, impasto brushstrokes to her canvases with a palette knife. Gual is a graduate of the Florence Academy of Art. She strives to transform classical approaches to anatomy, composition, and light into her own style. Also a self-taught photographer, Gual often creates paintings from her own photographs, exploring the relationship between the two disciplines.
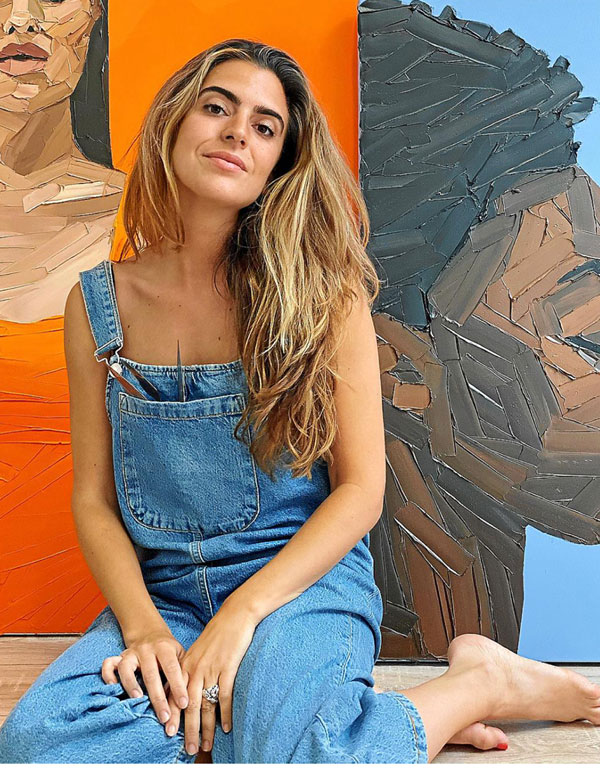

LARA PADILLA (Madrid, 1988)
Lara Padilla has a degree in Fine Arts from the Complutense University of Madrid and a Master's degree in Film Photography Direction from the TAI School. She has participated in solo and group exhibitions at national and international level, such as her recent solo exhibition at the Juan Silió Gallery or her participation in the last editions of the Santander 2023 and Art Basel Miami 2022 art fairs. In addition to her artistic career, she has made a name for herself as a fashion designer, collaborating with clients such as Springfield, Pepe Jeans and Levis. She also actively collaborates with Patricia Field, the stylist behind series such as Sex In The City and The Devil Wears Prada, for her Patricia Field Art Fashion project, creating unique hand-painted garments. Lara Padilla lives and works in Madrid, Miami and New York.
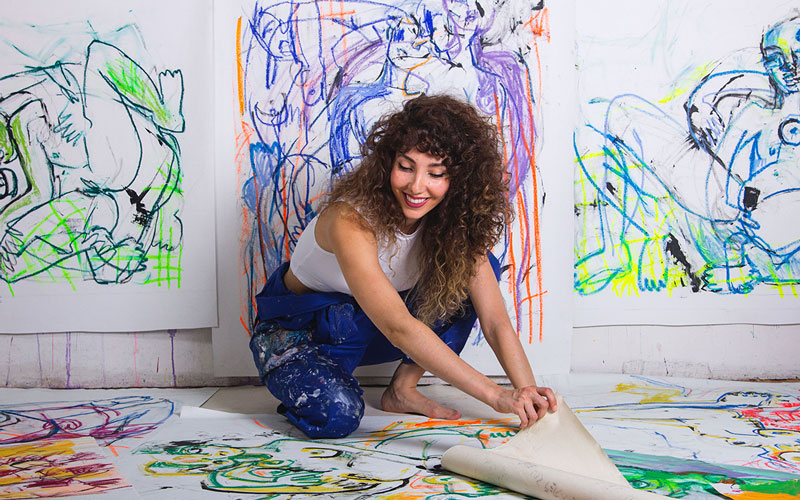

RICHARD GARCÍA (Madrid, 1995)
Richard García graduated in Fine Arts from the Complutense University of Madrid in the year 2017. After this stage, he began his journey as an artist, winning numerous competitions and beginning to develop his own style and discourse. The creative process is one of the most important parts of his work, in which he allows himself to be guided by intuition, through which he reflects superimposition and transparency.
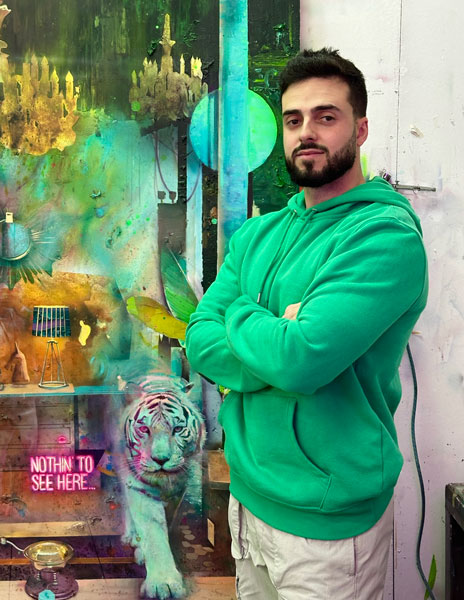

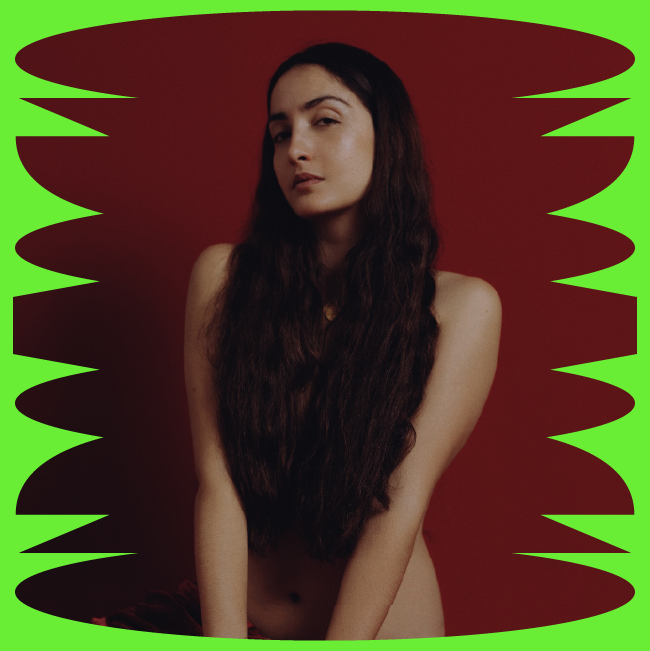
MARINA TELLME (Almería, 1995)
She has a degree in Fine Arts from the Alonso Cano Faculty (Granada) and a Masters in Film Directing from the TAI. She has also qualified as a voice actress at the EDM (Madrid). Her work has been exhibited at the Humboldt University (Berlin), the García Lorca Art Centre (Granada), the Bless Hotel (Madrid), the Instituto de la Mujer de Almería, selected at the Art Sur Festival of Art in Action (Córdoba) and the Femujer de Santo Domingo (Dominican Republic), among others.
Her art is the result of her passion for telling stories. Her paintings, sculptures and installations present a scenography (like a frame of an animated film) with characters and circumstances that are mostly comic and naïve in style, but with room for social criticism.